A group of phytonutrients known for providing color pigmentation to plants. Over 6,000 varieties of flavonoids have been found in nature, some of which are responsible for protecting plants against the elements, such as harmful UV raps, pests, and diseases. Cannabis flavonoids, called “cannaflavins,” play an important role in odor and flavor differences between strains. Similar to terpenes, flavonoids help us perceive cannabis through our senses.
Flavonoids (or bioflavonoids; from the Latin word flavus, meaning yellow, their color in nature) are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.
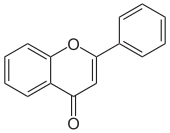
Chemically, flavonoids have the general structure of a 15-carbon skeleton, which consists of two phenyl rings (A and B) and a heterocyclic ring (C, the ring containing the embedded oxygen). This carbon structure can be abbreviated C6-C3-C6. According to the IUPAC nomenclature, they can be classified into:
- flavonoids or bioflavonoids
- isoflavonoids, derived from 3-phenylchromen-4-one (3-phenyl-1,4-benzopyrone) structure
- neoflavonoids, derived from 4-phenylcoumarine (4-phenyl-1,2-benzopyrone) structure
The three flavonoid classes above are all ketone-containing compounds and as such, anthoxanthins (flavones and flavonols). This class was the first to be termed bioflavonoids. The terms flavonoid and bioflavonoid have also been more loosely used to describe non-ketone polyhydroxy polyphenol compounds, which are more specifically termed flavanoids. The three cycles or heterocycles in the flavonoid backbone are generally called ring A, B, and C. Ring A usually shows a phloroglucinol substitution pattern.